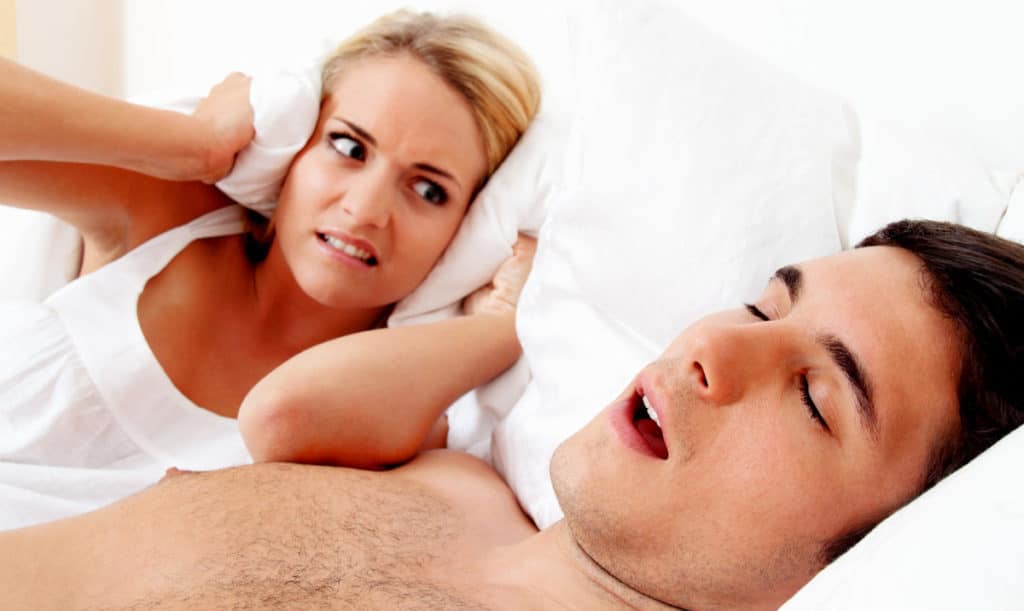
What You Should Know About Snoring
Just about everybody snores. However, in some cases, it can be an ongoing problem for the snorer and an annoyance for their bed partner. If you snore, you’ve got a lot of company when you consider up to 50% of all US adults snore. Even if doesn’t bother you, it’s not something you want to ignore. In some cases, snoring may be an indication of a more serious underlying condition including obesity, obstructive sleep apnea, sleep deprivation, or an anatomical or structural issue of the mouth, nose, or throat.
Snoring typically worsens with age. For example, 30% of individuals in the 30+ range snore while 40% of middle-aged individuals snore. Ironically, the occurrences of snoring in men 70 years of age and older tend to decrease. Here are some additional statistics about snoring:
- 25% of all individuals are regular snorers, 45% snore occasionally, and roughly 10% of children snore
- 40% of men are regular snorers while on 24% of women are
- 59% of snorers are aware of it
- 80% to 90% of snorers have difficulties reaching REM sleep
- Regular snorers have an elevated risk (up to 5 times higher) of developing some form of heart disease
- Snorers have an 80% elevated risk of developing insulin resistance, which means that they’re at risk of developing Type II diabetes
- Snoring is the 3rd leading cause of separation and divorce
- Women with snoring partners are 3 times more likely to suffer with insomnia.
Most of us know someone who snores or has had relationship problems associated with snoring. Thanks to modern technology, there are home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help you quit snoring as well as other types of snoring cures.
What is Snoring?
In the simplest of terms, snoring is the harsh breathing sound a person makes while sleeping. This sound occurs as the air you breathe flows past relaxed throat tissues, causing them to vibrate and make the snoring noise. When air is forced past a partial blockage or obstruction in the airway, the soft tissues in your mouth, nose, and throat vibrate by bumping into one another. These vibrations make the grumbling, rattling, or snorting sound which we commonly refer to as snoring.
It’s important to know what type of snorer you are in order to determine a cure for snoring that’s right for you. There are 4 types of snoring as follows:
- Mouth Snoring – results from breathing through the mouth rather than the nose. This type of snoring typically results from sleeping on your back and causes you to snore with an open mouth.
- Nose Snoring – blocked nostrils caused by a deviated septum or other obstruction in the nose blocks the airway and causes nose snoring. This can result in bad breath, dry mouth, and headaches.
- Throat Snoring – as the loudest and probably most dangerous snoring of all, throat snoring is usually associated with obstructive sleep apnea or OSA. Throat snorers snore regardless of their sleeping position. This type of snoring usually requires the attention of a healthcare professional or sleep therapist.
- Tongue Snoring – when lying on your back, the tongue has a greater tendency to relax and block airflow into the lungs. The difficulty breathing that results causes snoring. This type of snoring is characterized by high-pitched, inconsistent sounds.
No matter what type of snorer you are, you probably aren’t getting the quality of sleep that you should. Chances are, neither is your partner.
How can You tell if You have a Snoring Problem?
When you consider that 59% of all snorers aren’t aware that they snore (see above), it makes you wonder if there are ways to determine whether or not you have a snoringproblem. Fortunately, there are 5 ways to determine that as follows:
- Ask Your Partner – while this may seem obvious, sometimes the severity of a person’s snoring can’t be determined without some assistance. Asking someone, such as your partner or a roommate, to let you know if they hear you snoring will enable you to learn if you are and how severe the problem is.
- Be Aware of the Symptoms – if you still feel tired the next day after getting a full night’s rest, snoring might be the culprit. Snoring also causes daytime irritability, a sore throat, or trouble concentrating. No matter how insignificant you think these symptoms are, be sure to share them with your doctor.
- If Possible, Record Yourself Snoring while Sleeping – if you have access to a voice-activated recording device, try to record your snoring during sleep. This will provide you and your doctor or sleep therapist with useful information. Be sure to listen for pauses in your breathing as this may be an indication of OSA.
- Keep a Sleep Diary or Journal – start keeping a daily diary or journal that includes specific information such as what time you fell asleep, how long you slept, when you woke up, and why you woke up. If you’re aware of your sleeping habits, it will enable you to identify any inconsistencies.
- Visit a Doctor or Sleep Specialist – this is the most effective way to determine to find out if you have a snoring problem. A certified otolaryngologist can help with any snoring issues you may have and if it’s a symptom of a more serious condition.
Your physician may prescribe a sleep study to obtain more in-depth information and decide how serious the problem is as well as if medical attention is required. This will enable them to determine a cure for snoring that’s right for you.
Causes of Snoring
So, why do people snore? No two snorers are alike nor are the causes of their snoring. Consequently, if you want to find the right snoring cure, it’s important to know what is causing your snoring problem. Since snoring results from a blocked or restricted airway, there are several conditions and factors that can cause this including:
- anatomical or structural issues that decrease airway size (mouth, nose, or throat)
- drinking alcohol
- excess body fat, being overweight
- low muscle tone or weakened mouth, nose, or throat muscles
- nasal congestion and inflammation associated with allergies or airborne irritants, a cold, or the flu
- nasal inflammation caused by pregnancy hormones
- taking sedatives that help to relax the muscles
With the exception of anatomical and structural issues that narrow the airway, home remedies and lifestyle changes can help you eliminate the cause of your snoring.
How to Cure Snoring
In most cases, the treatment for snoring depends on the cause. There are non-surgical treatments for snoring such as lifestyle changes. However, the more severe cases may require a specific surgical procedure to correct the problem. Your doctor will probably recommend non-surgical snoring cures before going the more invasive surgical route. These include:
- Lifestyle changes such as avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime, changing your sleeping position, losing weight, etc.
- Medications for allergies and colds that help you breathe freely by relieving congestion
- Nasal strips that stick to the nose above the flare of each nostril and keep the nasal passages open
- Oral appliances that move the lower jaw forward and keep it in a position that enables constant airflow
If these remedies don’t work or your snoring gets worse, surgery may be recommended as a cure for snoring and sleep-disordered breathing. These procedures are employed to correct anatomical or structural problems and to remove or shrink excess tissue. These procedures include:
- Adenoidectomies and Tonsillectomies– Excess tissue is removed from the back of the nose or the back of the throat.
- Laser-assisted Uvulapalatoplasty (LAUP)– Improves airflow by reducing excess tissue from the soft palate.
- Radiofrequency Ablation– Also known as “Somnoplasty®”, this procedure utilizes radiofrequency energy to shrink excess soft palate and tongue tissue.
- Septoplasty– The procedure that’s employed to straighten a deviated septum by reshaping the bone and cartilage and improve airflow.
Natural Way to Cure Snoring
As was mentioned above, identifying the cause of snoring can be instrumental in learning how to cure snoring. The more natural remedies include:
- Avoid alcohol
- Change your diet habits and cut back on inflammatory foods
- Do exercises that strengthen throat and tongue muscles
- Don’t sleep on your back
- Drink more water
- Elevate the head of your bed
- Get enough sleep
- Lose weight
- Quit smoking
- Use a facial steam bowl or neti pot to open up airways
- Use a humidifier
Conclusion
Snoring is not only annoying and disruptive; it can also lead to other health problems depending on the severity of the problem. Therefore, it’s essential that you speak with your doctor or a sleep therapist about how to cure snoring and snoring cures. If your child has a snoring problem, speak with their pediatrician. If your child snores, they may not be getting enough restful sleep. Additionally, sleep deprivation in children increases their risk of behavioral problems.
Chronic or frequent snoring can also indicate or be a symptom of a more serious problem. Plus, long-term snoring can cause more serious health problems. If you have a snoring problem, try Asonor Anti-snoring Spray and Solution (proven effective in 3 out of every 4 cases). For additional information about this amazing product, visit the Asonor website or send us an e-mail by clicking here.
Also Read- Does Snoring Lead to Heart Disease?